Darius N. Couch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Darius Nash Couch (July 23, 1822 ŌĆō February 12, 1897) was an American soldier, businessman, and naturalist. He served as a career
 Couch then saw action with the U.S. Army during the
Couch then saw action with the U.S. Army during the

 Couch led his division during the
Couch led his division during the
 On November 14, 1862, Couch was assigned command of the II Corps, and he led it during the
On November 14, 1862, Couch was assigned command of the II Corps, and he led it during the
 Following the Union defeat at Fredericksburg and the inglorious Mud March in January 1863, the commander of the Army of the PotomacŌĆöCouch's immediate superiorŌĆöwas again replaced. Maj. Gen.
Following the Union defeat at Fredericksburg and the inglorious Mud March in January 1863, the commander of the Army of the PotomacŌĆöCouch's immediate superiorŌĆöwas again replaced. Maj. Gen.
 Couch returned to civilian life in Taunton after the war, where he ran unsuccessfully as a Democratic candidate for
Couch returned to civilian life in Taunton after the war, where he ran unsuccessfully as a Democratic candidate for
Vol. 1
an
Vol. 2
of the 1908.
Ćö
civilwarhome.com
Couch's official reports for the Fredericksburg Campaign.
''Massachusetts in the War, 1861ŌĆō1865''
Springfield, MA: C. W. Bryan & Co., 1888. . *
Darius Couch
ĆöGeorgia's Blue and Gray Trail site biography;
at historycentral.com * Photo gallery of Couch at www.generalsandbrevets.com {{DEFAULTSORT:Couch, Darius N. 1822 births 1897 deaths American military personnel of the MexicanŌĆōAmerican War American naturalists American people of the Seminole Wars Burials at Mount Pleasant Cemetery (Taunton, Massachusetts) Collectors of the Port of Boston Connecticut Adjutant Generals Massachusetts Democrats Members of the Aztec Club of 1847 Military personnel from Connecticut People from Norwalk, Connecticut People from Southeast, New York People from Taunton, Massachusetts People of Massachusetts in the American Civil War Scientists from New York (state) Union Army generals United States Military Academy alumni
U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
officer during the MexicanŌĆōAmerican War
The MexicanŌĆōAmerican War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, the Second Seminole War
The Second Seminole War, also known as the Florida War, was a conflict from 1835 to 1842 in Florida between the United States and groups collectively known as Seminoles, consisting of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans and ...
, and as a general officer
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED O ...
in the Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. st ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 ŌĆō May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
.
During the Civil War, Couch fought notably in the Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
and Fredericksburg campaigns of 1862, and the Chancellorsville and Gettysburg campaigns of 1863. He rose to command a corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies great ...
in the Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confedera ...
, and led divisions in both the Eastern Theater and Western Theater. Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
under his command played a strategic role during the Gettysburg Campaign in delaying the advance of Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
troops of the Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most oft ...
and preventing their crossing the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
, critical to Pennsylvania's defense.
He has been described as personally courageous, very thin in build, and (after his time in Mexico) frail of health.
Early life and career
Couch was born in 1822 on a farm in the village ofSoutheast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directionsŌĆönorth, east, south, and westŌĆöeach sepa ...
in Putnam County, New York
Putnam County is a county located in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 97,668. The county seat is Carmel. Putnam County formed in 1812 from Dutchess County and is named for Israel Putnam, a hero in the ...
, and was educated at the local schools there.Warner, ''Generals in Blue'', p. 95. In 1842 he entered the United States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a fort, since it sits on strategic high groun ...
at West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known Metonymy, metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a f ...
, graduating four years later 13th out of 59 cadets. On July 1, 1846, Couch was commissioned a brevet
Brevet may refer to:
Military
* Brevet (military), higher rank that rewards merit or gallantry, but without higher pay
* Brevet d'├®tat-major, a military distinction in France and Belgium awarded to officers passing military staff college
* Aircre ...
second lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until ...
and was assigned to the 4th U.S. Artillery.Eicher, ''Civil War High Commands'', p. 186.
MexicanŌĆōAmerican War
The MexicanŌĆōAmerican War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, most notably in the Battle of Buena Vista
The Battle of Buena Vista (February 22ŌĆō23, 1847), known as the Battle of La Angostura in Mexico, and sometimes as Battle of Buena Vista/La Angostura, was a battle of the MexicanŌĆōAmerican War. It was fought between the US invading forces, l ...
on February 22ŌĆō23, 1847. For his actions on the second day of this fight, he was brevetted a first lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment.
The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a s ...
for "gallant and meritorious conduct." After the war ended in 1848 Couch began serving in garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mil ...
duty at Fort Monroe
Fort Monroe, managed by partnership between the Fort Monroe Authority for the Commonwealth of Virginia, the National Park Service as the Fort Monroe National Monument, and the City of Hampton, is a former military installation in Hampton, Virgi ...
in Hampton, Virginia
Hampton () is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the population was 137,148. It is the List ...
. The following year he was stationed at Fort Pickens
Fort Pickens is a pentagonal historic United States military fort on Santa Rosa Island in the Pensacola, Florida, area. It is named after American Revolutionary War hero Andrew Pickens. The fort was completed in 1834 and was one of the few ...
, located near Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ...
, and then in Key West
Key West ( es, Cayo Hueso) is an island in the Straits of Florida, within the U.S. state of Florida. Together with all or parts of the separate islands of Dredgers Key, Fleming Key, Sunset Key, and the northern part of Stock Island, it cons ...
. Couch next participated in the Seminole Wars
The Seminole Wars (also known as the Florida Wars) were three related military conflicts in Geography of Florida, Florida between the United States and the Seminole, citizens of a Native Americans in the United States, Native American nation whi ...
during 1849 and into 1850.
Returning to garrison duty, later that year Couch was sent to Fort Columbus
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
in New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in t ...
, and in 1851 Couch was involved in recruiting at Jefferson Barracks
The Jefferson Barracks Military Post is located on the Mississippi River at Lemay, Missouri, south of St. Louis. It was an important and active U.S. Army installation from 1826 through 1946. It is the oldest operating U.S. military installation w ...
located on the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
at Lemay, Missouri
Lemay is a census-designated place (CDP) in south St. Louis County, Missouri, United States. The population was 16,645 at the 2010 census.
History
Lemay was named after Francois Lemai, who operated a ferry boat across the Meramec River in the e ...
. Later in 1851 he returned to Fort Columbus, and then was ordered to Fort Johnston in Southport, North Carolina, staying there into 1852, and next in garrison at Fort Mifflin
Fort Mifflin, originally called Fort Island Battery and also known as Mud Island Fort, was commissioned in 1771 and sits on Mud Island (or Deep Water Island) on the Delaware River below Philadelphia, Pennsylvania near Philadelphia International A ...
in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
until 1853.
Couch then took a one-year leave of absence from the army from 1853 to 1854 to conduct a scientific mission for the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
in northern Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: M├®xico), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. There, he discovered the species that are known as Couch's kingbird
Couch's kingbird (''Tyrannus couchii'') is a passerine tyrant flycatcher of the kingbird genus. It is found from southern Texas along the Gulf Coast to the Yucat├Īn Peninsula in Mexico, Belize and northern Guatemala. It is also found in the lower ...
and Couch's spadefoot toad
Couch's spadefoot toad or Couch's spadefoot (''Scaphiopus couchii)'' is a species of North American spadefoot toad (family Scaphiopodidae). The specific epithet ''couchii'' is in honor of American naturalist Darius Nash Couch, who collected ...
.Heidler, ''Encyclopedia of the American Civil War'', p. 505. Upon his return to the United States in 1854, Couch was ordered to Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, on detached service. Later that year he resumed garrison duty in Fort Independence at Castle Island along Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, and is located adjacent to the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the northeastern United States.
History
Since ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, m╔Öhswat╩ā╔Öwi╦És╔Öt'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
. Also in 1854 he was stationed at Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., an ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, and would remain there into the following year. On April 30, 1855, Couch resigned his commission in the U.S. Army. From 1855 to 1857 he was a merchant in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
. He then moved to Taunton, Massachusetts
Taunton is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the county seat, seat of Bristol County. Taunton is situated on the Taunton River which winds its way through the city on its way to Mount ...
, and worked as a copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
fabricator in the company owned by his wife's family. Couch was still working in Taunton when the American Civil War began in 1861.
American Civil War service
Early service
At the outbreak of the Civil War, Couch was appointed commander of the 7th Massachusetts Infantry on June 15, 1861, with the rank ofcolonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
in the Union Army. That August he was promoted to brigadier general
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
with an effective date back to May 17. He was given brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division.
Br ...
command in the Military Division then Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confedera ...
that fall, and Couch was given divisional command in the VI Corps 6 Corps, 6th Corps, Sixth Corps, or VI Corps may refer to:
France
* VI Cavalry Corps (Grande Arm├®e), a cavalry formation of the Imperial French army during the Napoleonic Wars
* VI Corps (Grande Arm├®e), a formation of the Imperial French army du ...
in the following spring. From July 1861 to March 1862 he helped train and then maintain the defenses of Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
He participated in the Peninsula Campaign, fighting in the Siege of Yorktown
The Siege of Yorktown, also known as the Battle of Yorktown, the surrender at Yorktown, or the German battle (from the presence of Germans in all three armies), beginning on September 28, 1781, and ending on October 19, 1781, at Yorktown, Virgi ...
on April 5ŌĆōMay 4 and the Battle of Williamsburg
The Battle of Williamsburg, also known as the Battle of Fort Magruder, took place on May 5, 1862, in York County, James City County, and Williamsburg, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the first pitc ...
the following day.
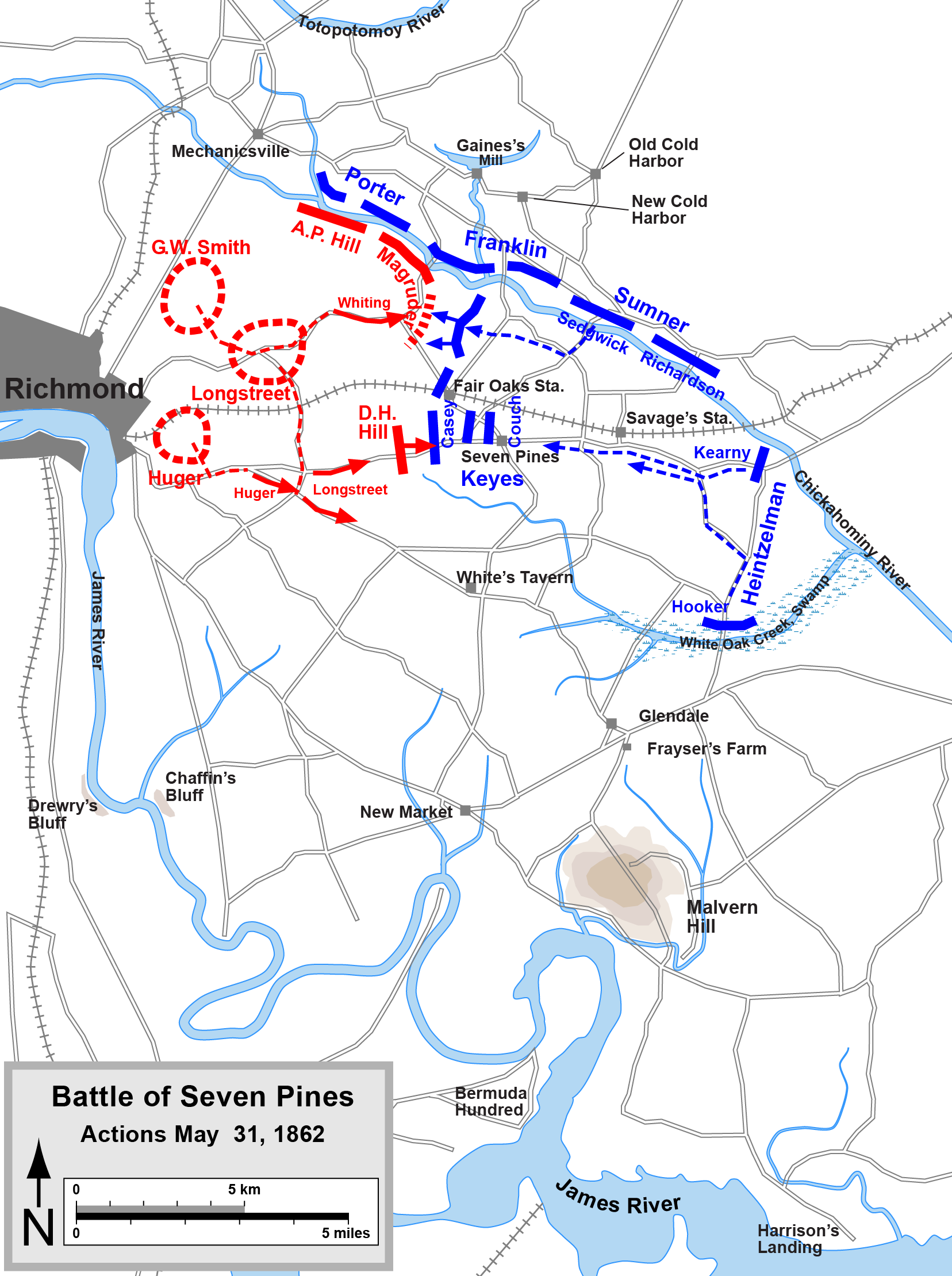
Seven Pines
 Couch led his division during the
Couch led his division during the Battle of Seven Pines
The Battle of Seven Pines, also known as the Battle of Fair Oaks or Fair Oaks Station, took place on May 31 and June 1, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, nearby Sandston, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was t ...
on May 31 and June 1, 1862. In this engagement his corps commander, Brig. Gen. Erasmus D. Keyes, ordered Couch's division and that of Brig. Gen. Silas Casey
Silas Casey (July 12, 1807 ŌĆō January 22, 1882) was a career United States Army officer who rose to the rank of major general during the American Civil War.
Early life and military career
Casey was born in East Greenwich, Rhode Island. He gradua ...
forward of the Union defensive line, Couch's men right behind those of Casey. This placed the IV Corps in an isolated position, vulnerable to attack on three sides; however poorly coordinated Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
movements allowed Couch and Casey to partially prepare entrenchments against the impending assault. As the fighting continued throughout May 31 both Couch and Casey were slowly driven back, with their right flank units in the most peril. At this time Couch counterattacked with his old 7th Massachusetts Infantry and the 62nd New York Infantry in an attempt to bolster that side, however he did not succeed and was forced back, as was the rest of the Union IV Corps by nightfall.
Couch continued to lead his division during the 1862 Seven Days Battles
The Seven Days Battles were a series of seven battles over seven days from June 25 to July 1, 1862, near Richmond, Virginia, during the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee drove the invading Union Army of the Potomac, command ...
that followed, fighting in the Battle of Oak Grove
The Battle of Oak Grove, also known as the Battle of French's Field or King's School House, took place on June 25, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, the first of the Seven Days Battles ( Peninsula Campaign) of the American Civil War. Maj. Gen. ...
on June 25 and the Battle of Malvern Hill
The Battle of Malvern Hill, also known as the Battle of Poindexter's Farm, was fought on July 1, 1862, between the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, led by Gen. Robert E. Lee, and the Union Army of the Potomac under Maj. Gen. George B. Mc ...
on July 1. Later in July Couch's health began to fail, prompting him to offer his resignation. The army commander, Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 ŌĆō October 29, 1885) was an American soldier, Civil War Union general, civil engineer, railroad executive, and politician who served as the 24th governor of New Jersey. A graduate of West Point, McCl ...
, refused to send it to the U.S. War Department
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department (and occasionally War Office in the early years), was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army, a ...
, and instead Couch was promoted to major general
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
, to date from July 4. Couch was involved in the Maryland Campaign that fall, although absent from the Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam (), or Battle of Sharpsburg particularly in the Southern United States, was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862, between Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union G ...
on September 17.
Fredericksburg
 On November 14, 1862, Couch was assigned command of the II Corps, and he led it during the
On November 14, 1862, Couch was assigned command of the II Corps, and he led it during the Battle of Fredericksburg
The Battle of Fredericksburg was fought December 11ŌĆō15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. The combat, between the Union Army of the Potomac commanded by Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnsi ...
as part of Maj. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner's "Right Grand Division". In this fight Couch's corps contained three divisions, led by Brig. Gens. Winfield Scott Hancock
Winfield Scott Hancock (February 14, 1824 ŌĆō February 9, 1886) was a United States Army officer and the Democratic nominee for President of the United States in 1880. He served with distinction in the Army for four decades, including service ...
, Oliver Otis Howard
Oliver Otis Howard (November 8, 1830 ŌĆō October 26, 1909) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the Civil War. As a brigade commander in the Army of the Potomac, Howard lost his right arm while leading his men agains ...
, and William H. French. Early on December 12 infantry from his corps attempted to support the Union engineers' efforts to lay pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge (or ponton bridge), also known as a floating bridge, uses float (nautical), floats or shallow-draft (hull), draft boats to support a continuous deck for pedestrian and vehicle travel. The buoyancy of the supports limits the maxi ...
s across the Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 It traverses the entir ...
and into the town. When Confederate fire repeatedly prevented this, and a heavy artillery bombardment failed as well, the decision was made to send small groups of soldiers across in pontoon boats to dislodge the defenders. This amphibious assault
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducted ...
, which finally succeeded in driving out the Confederates, was executed by one of Couch's brigades under Col. Norman J. Hall (3rd Brigade, 2nd Division ŌĆō 19th & 20th Massachusetts, 7th Michigan, 42nd & 59th New York, & 127th Pennsylvania).
As the Union soldiers entered a smoldering Fredericksburg they began to sack the city, forcing Couch to order his provost guard to secure the bridges and collect the loot. The next day his corps was ordered to attack the Confederate position at the base of Marye's Heights above Fredericksburg. To better watch his men's progress Couch entered the town's courthouse and climbed its cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, from ...
, where he could see French's division advancing. As they approached the Confederate defenses, Couch could see his men taking very heavy fire and easily repulsed, described "as if the division had simply vanished." Hancock's division followed that of French, meeting the same fate with high casualties as well. Howard, who was to go in next, was with Couch as Hancock's division attacked. Briefly through the smoke they could see the mounting casualties, and Couch reportedly said, "Oh, great God! See how our men, our poor fellows, are falling."
Couch ordered Howard to march his division toward the right and possibly flank
Flank may refer to:
* Flank (anatomy), part of the abdomen
** Flank steak, a cut of beef
** Part of the external anatomy of a horse
* Flank speed, a nautical term
* Flank opening, a chess opening
* A term in Australian rules football
* The si ...
the Confederate defenses his other two divisions had failed to dislodge. However the terrain did not permit any force that was marching from Fredericksburg toward Marye's Heights to attack anywhere other than at the stone wall along its base. When Howard's men attacked they were crowded back to the left, meeting the same resistance, and were repulsed. As other Union soldiers followed the II Corps in, Couch ordered his artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
to move into the field and blast the Confederates at close range. When his own artillery chief protested against exposing the gun crews in this fashion, Couch stated that he agreed but it was necessary to slow the Confederate fire in some way. The cannon stopped about 150 yards from the stone wall and opened fire, but quickly lost most of their crews and did little to slacken the enemy fire. During this time Couch moved slowly along his line of men, who were on the ground firing as best they could until nightfall. Recounting the attack on the heights on December 13, Couch wrote after the war:
In the attack Couch's force suffered heavily, as did the rest of the Right Grand Division. He reported that the II Corps sustained over four thousand casualties during the Fredericksburg Campaign. French's division lost an estimated 1,200 soldiers and Hancock around 2,000. Howard lost about 850 men, 150 of which were hit on December 11 supporting the engineers at the river. That night the Union wounded remained in the field, and Couch wrote after the war what he saw: "It was a night of dreadful suffering. Many died of wounds & exposure, and as fast as men died they stiffened in the wintry air, & on the front line were rolled forward for protection to the living. Frozen men were placed for dumb sentries."
Chancellorsville
 Following the Union defeat at Fredericksburg and the inglorious Mud March in January 1863, the commander of the Army of the PotomacŌĆöCouch's immediate superiorŌĆöwas again replaced. Maj. Gen.
Following the Union defeat at Fredericksburg and the inglorious Mud March in January 1863, the commander of the Army of the PotomacŌĆöCouch's immediate superiorŌĆöwas again replaced. Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Everett Burnside (May 23, 1824 ŌĆō September 13, 1881) was an American army officer and politician who became a senior Union general in the Civil War and three times Governor of Rhode Island, as well as being a successful inventor ...
was relieved and Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker
Joseph Hooker (November 13, 1814 ŌĆō October 31, 1879) was an American Civil War general for the Union, chiefly remembered for his decisive defeat by Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Chancellorsville in 1863.
Hooker had serv ...
named to his place. Hooker reorganized the army and drew up plans for a new campaign against the Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most oft ...
. He wished to avoid attacking the Confederate defenses at Fredericksburg and sought to flank them out of position, thereby fighting on more open ground. After the reorganization Couch continued to lead the II Corps, with his divisions commanded by Hancock and French (both now major generals) and Brig. Gen. John Gibbon
John Gibbon (April 20, 1827 – February 6, 1896) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the American Civil War and the Indian Wars.
Early life
Gibbon was born in the Holmesburg section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the fourt ...
at the head of Howard's former division, a total of about 17,000 soldiers.
During the ensuing Chancellorsville Campaign
The Battle of Chancellorsville, April 30 ŌĆō May 6, 1863, was a major battle of the American Civil War (1861ŌĆō1865), and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville campaign.
Chancellorsville is known as Lee's "perfect battle" because h ...
Couch was the senior corps commander, making him Hooker's second-in-command. In late April, Hooker began moving his corps across the Rappahannock and Rapidan River
The Rapidan River, flowing U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 through north-central Virginia in the United States, is the largest tributary of the Rappahannock ...
s, ordering two of Couch's divisions to entrench and defend the Banks's Ford crossing of the Rappahannock and detach Gibbon's 5,000 men to remain at the Union camp back at Falmouth on April 29. The following day Couch had cleared the ford and was marching toward Chancellorsville. In the afternoon of May 1 HookerŌĆönormally quite aggressiveŌĆöcautiously slowed his marching army, and soon he stopped their movement altogether, despite some success against the Confederates and the loud protests of his corps commanders. Couch sent Hancock's division to bolster the Union men already engaged, and informed Hooker they could handle the enemy in front of them. However, Hooker's orders stood; march back into the positions they held the previous day and assume a defensive posture. Couch complied and ordered Hancock's division to form a rear guard
A rearguard is a part of a military force that protects it from attack from the rear, either during an advance or withdrawal. The term can also be used to describe forces protecting lines, such as communication lines, behind an army. Even more ...
as they withdrew. As Hancock formed his men, Couch could see Confederate artillery aiming for the massed Union columns, and he told his staff "Let us draw their fire." The group of mounted officers clustered around a clearing where the enemy cannon could easily view them, thus attracting their fire and sparing the marching infantry; Couch and his staff also went unharmed. By nightfall the Union soldiers were busy fortifying the ground. Couch formed his divisions behind the XII Corps 12th Corps, Twelfth Corps, or XII Corps may refer to:
* 12th Army Corps (France)
* XII Corps (Grande Arm├®e), a corps of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* XII (1st Royal Saxon) Corps, a unit of the Imperial German Army
* XII ...
in roughly the center of Hooker's line.
By late afternoon on May 2, Hooker's line was hit on the right (the XI Corps 11 Corps, 11th Corps, Eleventh Corps, or XI Corps may refer to:
* 11th Army Corps (France)
* XI Corps (Grande Arm├®e), a unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* XI Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army
* ...
led by Howard) by Confederates under Lt. Gen. Thomas Jonathan "Stonewall" Jackson, and despite resisting the XI Corps was routed and ran toward Chancellorsville. The remaining corps tightened into a "U" shaped formation by May 3, and Confederate artillery began shelling their positions, including Couch's men. At about 9 a.m. that day Hooker was stunned by enemy fire when a shell hit the pillar he was leaning on, temporarily incapacitating him within an hour. At that time Hooker turned command of the army over to Couch, and through consulting with a "groggy" Hooker it was decided to withdraw the army to defensive lines to the north, with the other commanders (except an embarrassed Howard) strongly advocating an attack instead.
Gettysburg
Couch requested reassignment after quarreling with Hooker.President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966ŌĆō2010 Japanese ful ...
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 ŌĆō April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
offered him command of the Army of the Potomac, but he declined, citing poor health. He commanded the newly created Department of the Susquehanna The Department of the Susquehanna was a military department created by the United States War Department during the Gettysburg Campaign of the American Civil War. Its goal was to protect the state capital and the southern portions of the commonwealt ...
during the Gettysburg Campaign in 1863. Fort Couch in Lemoyne, Pennsylvania, was constructed under his direction and was named in his honor. Assigned to protect Harrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the List of c ...
from a threatened attack by Confederates under Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell
Richard Stoddert Ewell (February 8, 1817 – January 25, 1872) was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general during the American Civil War. He achieved fame as a senior commander under Stonewall Jackson and Robert E. L ...
, Couch directed militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
from his department to skirmish with enemy cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
elements at Sporting Hill, one of the war's northernmost engagements. Couch's militia then joined the pursuit of Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most oft ...
into Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
after the Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1ŌĆō3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
.
Subsequent activities
Confederates again invaded Couch's Department of the Susquehanna in August 1864, as Brig. Gen.John McCausland
John McCausland, Jr. (September 13, 1836 – January 22, 1927) was a brigadier general in the Confederate army, famous for the ransom of Hagerstown, Maryland, and the razing of Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, during the American Civil War.
Early ...
burned the town of Chambersburg
Chambersburg is a borough in and the county seat of Franklin County, in the South Central region of Pennsylvania, United States. It is in the Cumberland Valley, which is part of the Great Appalachian Valley, and north of Maryland and the Mas ...
. In December, Couch returned to the front lines with an assignment to the Western Theater, where he commanded a division in the XXIII Corps of the Army of the Ohio
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.
History
1st Army of the Ohio
General Orders No. 97 appointed Maj. Gen. Do ...
in the Franklin-Nashville Campaign and for the remainder of the war. Couch finished his military service after the Carolinas Campaign
The campaign of the Carolinas (January 1 ŌĆō April 26, 1865), also known as the Carolinas campaign, was the final campaign conducted by the United States Army (Union Army) against the Confederate States Army in the Western Theater. On January 1 ...
in 1865.
Postbellum career and death
 Couch returned to civilian life in Taunton after the war, where he ran unsuccessfully as a Democratic candidate for
Couch returned to civilian life in Taunton after the war, where he ran unsuccessfully as a Democratic candidate for Governor of Massachusetts
The governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the chief executive officer of the government of Massachusetts. The governor is the head of the state cabinet and the commander-in-chief of the commonwealth's military forces.
Massachusetts ...
in 1865. He later briefly served as president of a mining company in West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
. Couch moved to Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
in 1871, where he served as the Quartermaster General, and then Adjutant General, for the state militia until 1884. In 1888 he joined the Aztec Club of 1847
The Aztec Club of 1847 is a military society founded in 1847 by United States Army officers of the MexicanŌĆōAmerican War. It exists as a hereditary organization including members who can trace a direct lineal connection to those originally eligib ...
by right of his service in the Mexican War. He also joined the Connecticut Society of the Sons of the American Revolution
The National Society of the Sons of the American Revolution (SAR or NSSAR) is an American Congressional charter, congressionally chartered organization, founded in 1889 and headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky, Louisville, Kentucky. A non-prof ...
in 1890.
He died in Norwalk, Connecticut
, image_map = Fairfield County Connecticut incorporated and unincorporated areas Norwalk highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 230px
, map_caption = Location in Fairfield County, Connecticut, Fairfield County and ...
. He was buried in Mount Pleasant Cemetery in Taunton.
Legacy
According to Herman Hattaway and Michael D. Smith:Couch is best remembered as an able division and corps commander in the Army of the Potomac. His career occasionally was marred by personal traits of impatience and temper directed at both subordinates and superiors. He also suffered from prolonged bouts of ill health, which led to his acceptance of the post of department commander.In 2017, General Couch's portrait was featured on a mural in Lemoyne, Pennsylvania in commemoration of the defenses mounted in the town under his name during the Gettysburg campaign. The fort served as the last line of defense for Pennsylvania' capital city of Harrisburg. Couch is commemorated in the scientific names of two species of reptiles: '' Sceloporus couchii'' and '' Thamnophis couchii'', and one frog: '' Scaphiopus couchii''. He also has one bird species named for him:
Couch's kingbird
Couch's kingbird (''Tyrannus couchii'') is a passerine tyrant flycatcher of the kingbird genus. It is found from southern Texas along the Gulf Coast to the Yucat├Īn Peninsula in Mexico, Belize and northern Guatemala. It is also found in the lower ...
.
See also
*List of American Civil War generals (Union)
Union generals
__NOTOC__
The following lists show the names, substantive ranks, and brevet ranks (if applicable) of all general officers who served in the United States Army during the Civil War, in addition to a small selection of lower-ranke ...
* List of Massachusetts generals in the American Civil War
There were approximately 120 general officers from Massachusetts who served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. This list consists of generals who were either born in Massachusetts or lived in Massachusetts when they joined the army (i ...
* Massachusetts in the American Civil War
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts played a significant role in national events prior to and during the American Civil War (1861-1865). Massachusetts dominated the early antislavery movement during the 1830s, motivating activists across the nation. ...
Citations
General and cited references
* Alexander, Edward P. ''Fighting for the Confederacy: The Personal Recollections of General Edward Porter Alexander''. Edited byGary W. Gallagher
Gary William Gallagher is an American historian specializing in the history of the American Civil War. Gallagher is currently the John L. Nau III Professor in the History of the American Civil War at the University of Virginia. He produced a ...
. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1989. .
* Catton, Bruce. ''Glory Road''. Garden City, NY: Doubleday and Company, 1952. .
* Dupuy, Trevor N., Curt Johnson, and David L. Bongard. ''The Harper Encyclopedia of Military Biography''. New York: HarperCollins, 1992. .
* Eicher, David J. ''The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. .
* Eicher, John H., and David J. Eicher. ''Civil War High Commands''. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2001. .
* Foote, Shelby. '' The Civil War: A Narrative''. Vol. 2, ''Fredericksburg to Meridian''. New York: Random House, 1958. .
* Fredriksen, John C. ''Civil War Almanac''. New York: Checkmark Books, 2008. .
* Gambone, A. M. ''Major General Darius Nash Couch: Enigmatic Valor''. Baltimore: Butternut & Blue, 2000. .
* Heidler, David S., and Jeanne T. Heidler. "Darius Nash Couch." In ''Encyclopedia of the American Civil War: A Political, Social, and Military History'', edited by David S. Heidler and Jeanne T. Heidler. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2000. .
* Warner, Ezra J. ''Generals in Blue: Lives of the Union Commanders''. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1964. .
* Winkler, H. Donald. ''Civil War Goats and Scapegoats''. Nashville, TN: Cumberland House Publishing, 2008. .
* ''The Union Army: A History of Military Affairs in the Loyal States, 1861ŌĆō65ŌĆöRecords of the Regiments in the Union ArmyŌĆöCyclopedia of BattlesŌĆöMemoirs of Commanders and Soldiers''. Wilmington, NC: Broadfoot Publishing, 1997. First published 1908 by Federal Publishing CompanyVol. 1
an
Vol. 2
of the 1908.
Ćö
Aztec Club of 1847
The Aztec Club of 1847 is a military society founded in 1847 by United States Army officers of the MexicanŌĆōAmerican War. It exists as a hereditary organization including members who can trace a direct lineal connection to those originally eligib ...
site biography of Couch.
civilwarhome.com
Couch's official reports for the Fredericksburg Campaign.
Further reading
* Bowen, James Lorenzo''Massachusetts in the War, 1861ŌĆō1865''
Springfield, MA: C. W. Bryan & Co., 1888. . *
External links
Darius Couch
ĆöGeorgia's Blue and Gray Trail site biography;
at historycentral.com * Photo gallery of Couch at www.generalsandbrevets.com {{DEFAULTSORT:Couch, Darius N. 1822 births 1897 deaths American military personnel of the MexicanŌĆōAmerican War American naturalists American people of the Seminole Wars Burials at Mount Pleasant Cemetery (Taunton, Massachusetts) Collectors of the Port of Boston Connecticut Adjutant Generals Massachusetts Democrats Members of the Aztec Club of 1847 Military personnel from Connecticut People from Norwalk, Connecticut People from Southeast, New York People from Taunton, Massachusetts People of Massachusetts in the American Civil War Scientists from New York (state) Union Army generals United States Military Academy alumni